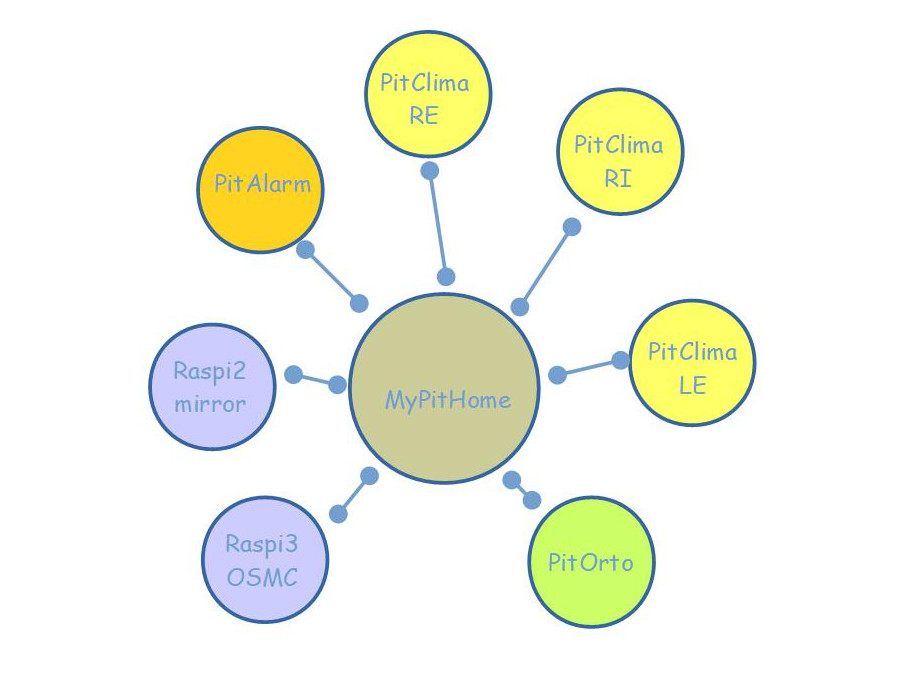
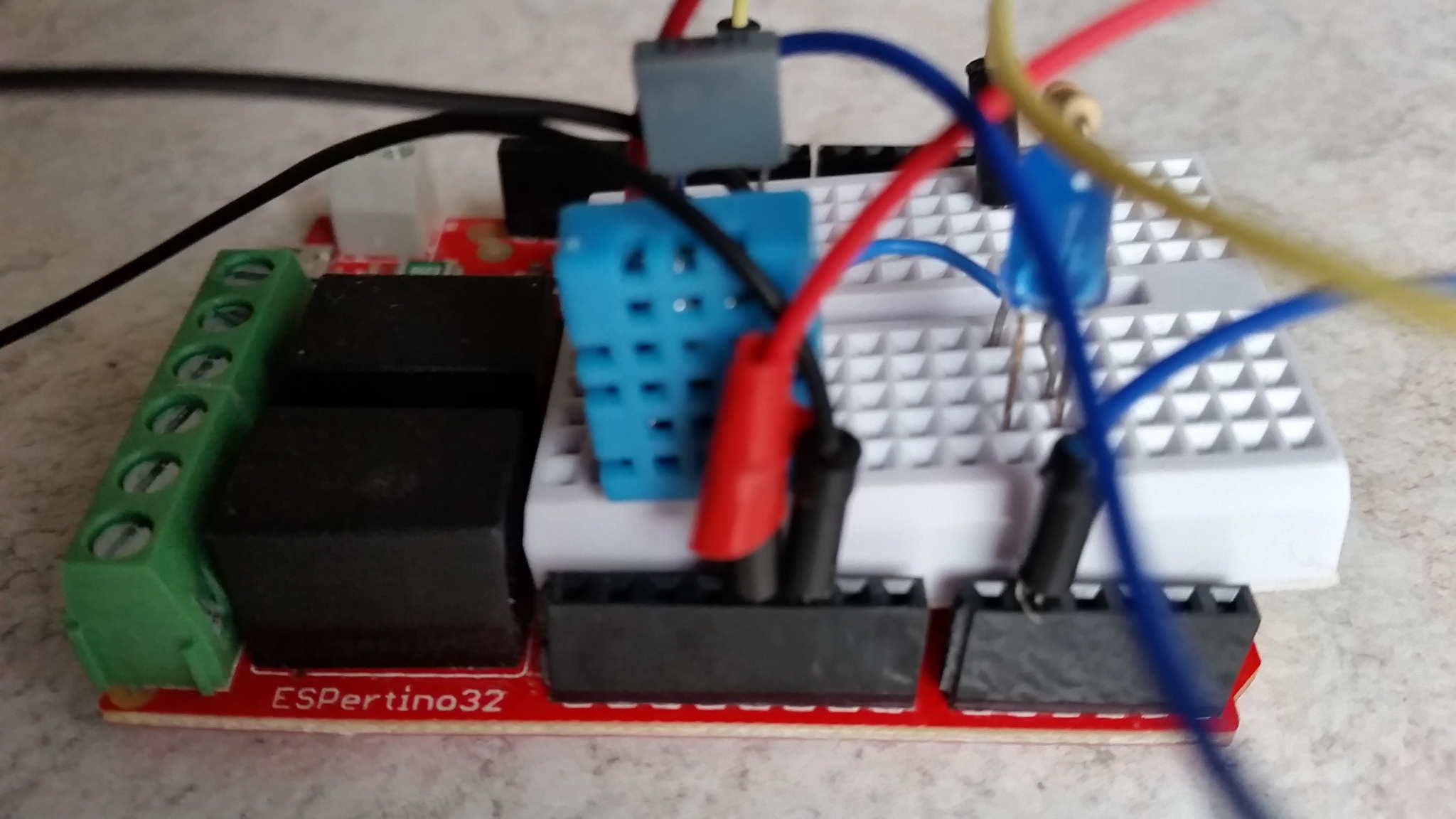
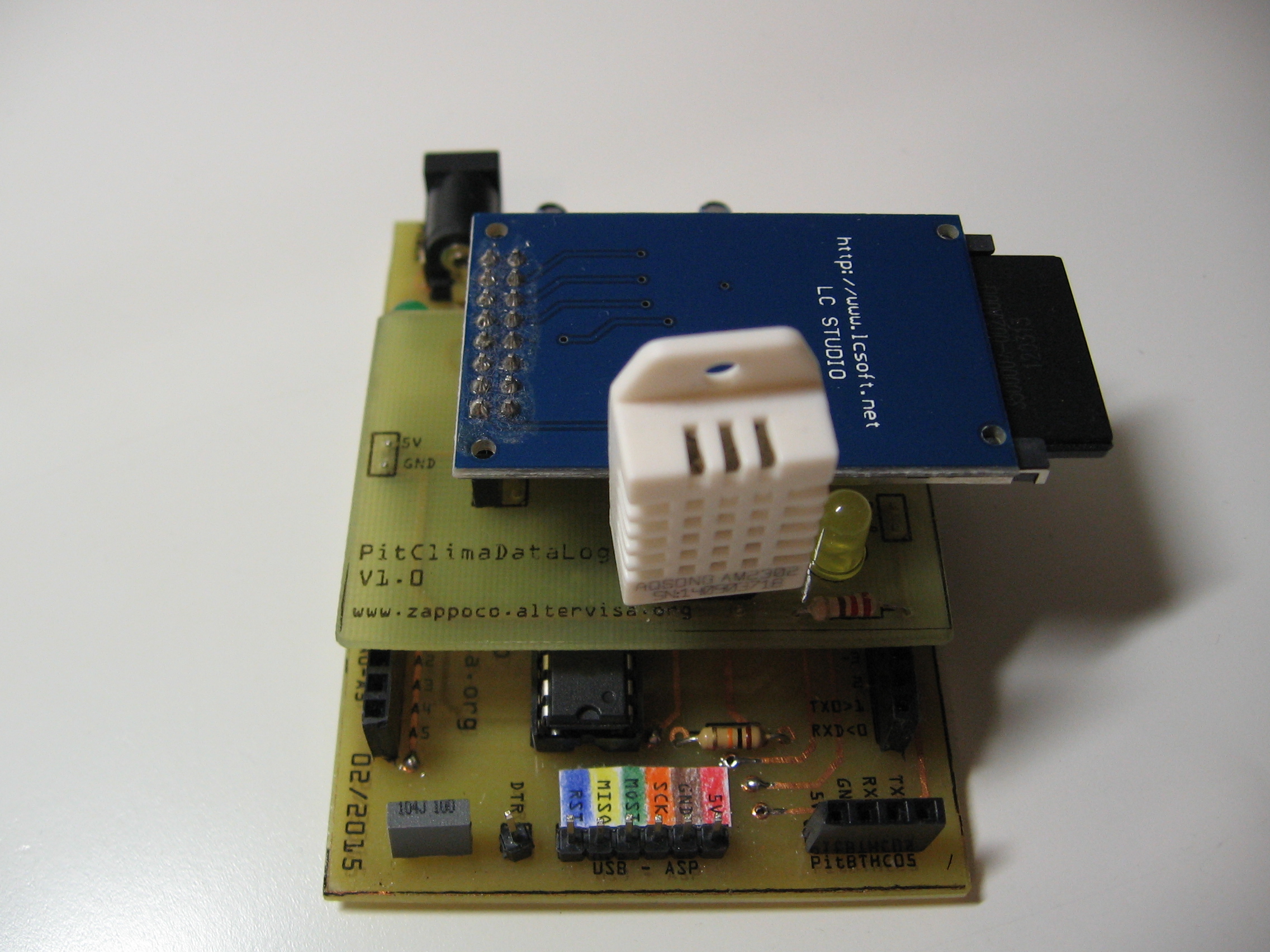
PitBME280 - Sensore di pressione, temperatura e umidità BME280
L'utilizzo del sensore di pressione, temperatura e umidità BME280.

E' stato integrato anche il calcolo della pressione a livello mare. E' stata dapprima riportato il calcolo con la formula presente nella libreria BME180 e poi per verifica è stata richiamata la specifica funzione della libreria BME280.
Cosa serve:
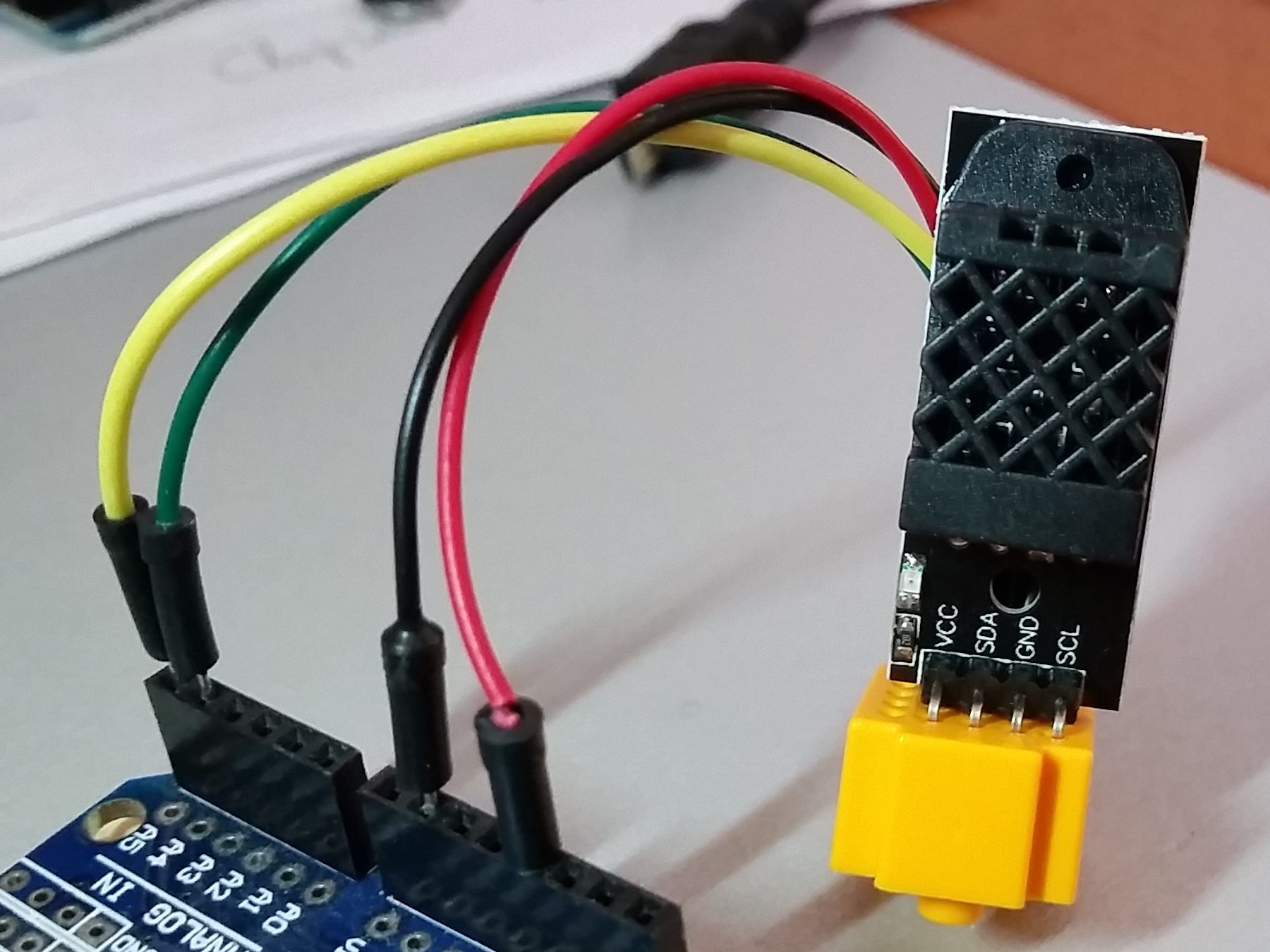
- Sensore BME280
- cavetti
Codice sorgente:
/***************************************************************************
This is a library for the BME280 humidity, temperature & pressure sensor
Designed specifically to work with the Adafruit BME280 Breakout
----> http://www.adafruit.com/products/2650
These sensors use I2C or SPI to communicate, 2 or 4 pins are required
to interface. The device's I2C address is either 0x76 or 0x77.
Adafruit invests time and resources providing this open source code,
please support Adafruit andopen-source hardware by purchasing products
from Adafruit!
Written by Limor Fried & Kevin Townsend for Adafruit Industries.
BSD license, all text above must be included in any redistribution
Istruzioni di Daniele Alberti
Per farlo funzionare ho dovuto modificare l'indirizzo I2C nella libreria.
E' una modifica piuttosto semplice, vi basterà infatti recarvi nella cartella di Arduino dove sono salvate
le librerie ed aprire il file "Adafruit_BMP280.h" (io ho usato Notepad++).
Modificate la riga 37 , da 0x77 a 0x76.
***************************************************************************/
#include "Wire.h"
#include "SPI.h"
#include "Adafruit_Sensor.h"
#include "Adafruit_BME280.h"
//#define BME_SCK 13
//#define BME_MISO 12
//#define BME_MOSI 11
//#define BME_CS 10
#define SEALEVELPRESSURE_HPA (1013.25)
Adafruit_BME280 bme; // I2C
//Adafruit_BME280 bme(BME_CS); // hardware SPI
//Adafruit_BME280 bme(BME_CS, BME_MOSI, BME_MISO, BME_SCK); // software SPI
unsigned long delayTime;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println(F("BME280 test"));
bool status;
// default settings
// (you can also pass in a Wire library object like &Wire2)
status = bme.begin();
if (!status) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BME280 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1);
}
Serial.println("-- Default Test --");
delayTime = 3000;
Serial.println();
}
void loop() {
printValues();
delay(delayTime);
}
void printValues() {
Serial.print("Temperature = ");
Serial.print(bme.readTemperature());
Serial.println(" *C");
Serial.print("Pressure = ");
double P = bme.readPressure(); //pressione relativa
//Serial.print(bme.readPressure() / 100.0F);
Serial.print(P / 100.0F);
Serial.println(" hPa");
#define ALTITUDINE 204 // serve per calcolare trasformare la pressione a livello mare
//
// formula presente nella libreria del BMP180 per il calcolo
// della pressione a livello mare
//
//
// Given a pressure P (mb) taken at a specific altitude (meters),
// return the equivalent pressure (mb) at sea level.
// This produces pressure readings that can be used for weather measurements.
//
// double SFE_BMP180::sealevel(double P, double A) {
// return(P/pow(1-(A/44330.0),5.255));
// }
double P0 = P / pow(1-( ALTITUDINE /44330.0),5.255);
Serial.print("Pressure SEA Level = ");
Serial.print(P0 / 100.0F);
Serial.println(" hPa");
Serial.print("Approx. Altitude = ");
Serial.print(bme.readAltitude(SEALEVELPRESSURE_HPA));
Serial.println(" m");
//
// pressione al livello mare calcolata con la funzione della libreria
//
Serial.print("Pressure SEA LEVEL = ");
Serial.print(bme.seaLevelForAltitude(ALTITUDINE, P) / 100.0F);
Serial.println(" hPa");
Serial.print("Humidity = ");
Serial.print(bme.readHumidity());
Serial.println(" %");
Serial.println();
}
Codice sorgente dello scanner I2C:
// i2c_scanner
//
// Version 1
// This program (or code that looks like it)
// can be found in many places.
// For example on the Arduino.cc forum.
// The original author is not know.
// Version 2, Juni 2012, Using Arduino 1.0.1
// Adapted to be as simple as possible by Arduino.cc user Krodal
// Version 3, Feb 26 2013
// V3 by louarnold
// Version 4, March 3, 2013, Using Arduino 1.0.3
// by Arduino.cc user Krodal.
// Changes by louarnold removed.
// Scanning addresses changed from 0...127 to 1...119,
// according to the i2c scanner by Nick Gammon
// http://www.gammon.com.au/forum/?id=10896
// Version 5, March 28, 2013
// As version 4, but address scans now to 127.
// A sensor seems to use address 120.
//
//
// This sketch tests the standard 7-bit addresses
// Devices with higher bit address might not be seen properly.
//
#include "Wire.h"
void setup()
{
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("\nI2C Scanner");
}
void loop()
{
byte error, address;
int nDevices;
Serial.println("Scanning...");
nDevices = 0;
for(address = 1; address < 127; address++ )
{
// The i2c_scanner uses the return value of
// the Write.endTransmisstion to see if
// a device did acknowledge to the address.
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
error = Wire.endTransmission();
if (error == 0)
{
Serial.print("I2C device found at address 0x");
if (address<16)
Serial.print("0");
Serial.print(address,HEX);
Serial.println(" !");
nDevices++;
}
else if (error==4)
{
Serial.print("Unknow error at address 0x");
if (address<16)
Serial.print("0");
Serial.println(address,HEX);
}
}
if (nDevices == 0)
Serial.println("No I2C devices found\n");
else
Serial.println("done\n");
delay(5000); // wait 5 seconds for next scan
}