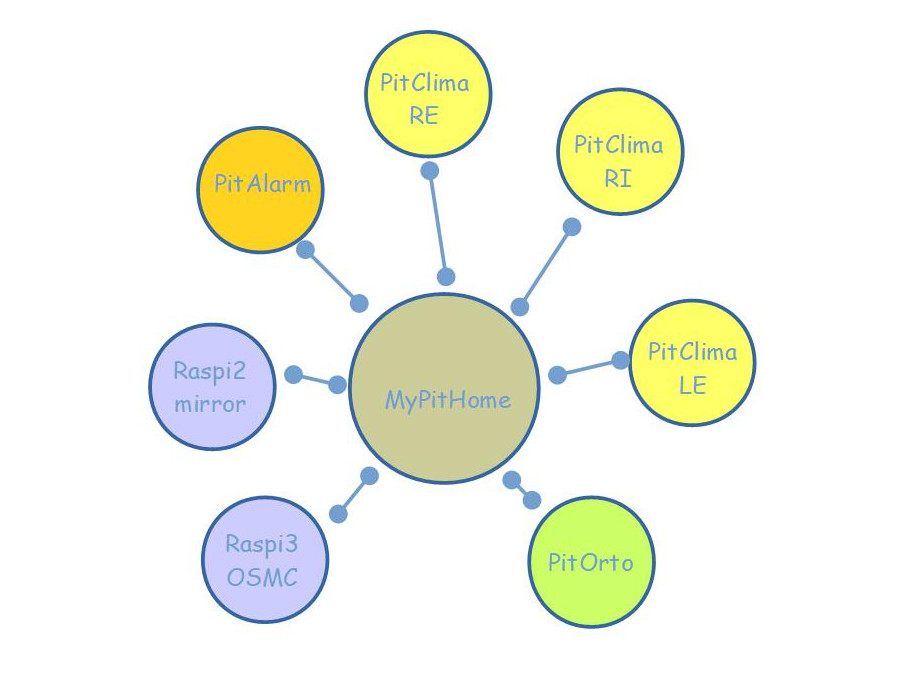
PitHCSR04
L'utilizzo del sensore ad ultrasuoni HC-SR04.

Prova del Sensore
Cosa serve:
- Sensore ad ultrasuoni HC-SR04
- cavetti
Codice sorgente:
//Adapted from David A. Mellis' code for Ping sensor
const int trigPin = 7;
const int echoPin = 4;
void setup() {
// initialize serial communication:
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(trigPin,OUTPUT);
pinMode(echoPin,INPUT);
}
void loop()
{
long duration, inches, cm;
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(5);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH);
Serial.print(trigPin);
Serial.print(" trigPin, ");
Serial.print(echoPin);
Serial.print(" echoPin, ");
Serial.print(duration);
Serial.print(" duration, ");
//Serial.println();
// convert the time into a distance
inches = microsecondsToInches(duration);
cm = microsecondsToCentimeters(duration);
Serial.print(inches);
Serial.print("in, ");
Serial.print(cm);
Serial.print("cm");
Serial.println();
delay(1000);
}
long microsecondsToInches(long microseconds)
{
// According to Parallax's datasheet for the PING))), there are
// 73.746 microseconds per inch (i.e. sound travels at 1130 feet per
// second). This gives the distance travelled by the ping, outbound
// and return, so we divide by 2 to get the distance of the obstacle.
// See: http://www.parallax.com/dl/docs/prod/acc/28015-PING-v1.3.pdf
return microseconds / 74 / 2;
}
long microsecondsToCentimeters(long microseconds)
{
// The speed of sound is 340 m/s or 29 microseconds per centimeter.
// The ping travels out and back, so to find the distance of the
// object we take half of the distance travelled.
return microseconds / 29 / 2;
}
Scarica tutto quello che serve:
ZappocoS, 7 febbraio 2018